BRIEF ABOUT DNS :
Either you are a web admin or know nothing about the technology, every person who use the internet has heard about this word domain name. But lots of people around us don’t know the purpose behind it. Let’s have a brief talk about it.
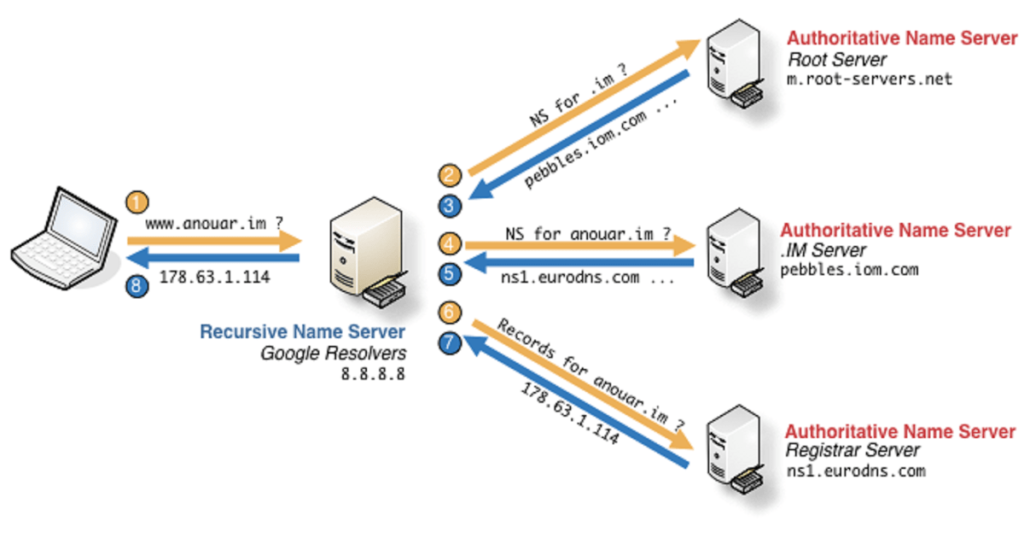
Suppose you write www.ethicaldebuggers.com in your browser. The very first thing you will see after the URL has been processed completely, is the homepage of our website. Have you ever thought what happens exactly? In the background, your client-browser has a resolver which is also known as stub resolver, it quickly finds if it has the DNS records that matches to the given domain name and if not, then this stub resolver queries for the given domain name records, also known as DNS records to your recursive resolver which ever is configured in your system. Usually router’s IP address is configured as the DNS resolver (or you can configure either google DNS 8.8.8.8 or Clouflare DNS resolver 1.1.1.1). These resolvers are the recursive resolver which means that they can query any other resolver on behalf of you and returns the IP address of the server where the website corresponding to that domain name is hosted, by resolving the whole domain name at each level i.e- root, Top Level Domain and name server of your domain. Finally, then your client queries the gateway and a connection is established between the client and the server. This whole name resolution system is known as Domain Name System.
WHAT IS GNS?
GNS- GNU Domain System is an implementation of GNUnet project as a completely decentralized and censorship-free DNS replacement. As announced earlier this year, GNUnet is a free open source software which is designed for peer to peer networking. GNUnet supports the creation of P2P (peer to peer) networks over TCP, UDP, HTTP / HTTPS, Bluetooth and WLAN, and can work in F2F (Friend-to-friend) mode. It uses NAT bypass including UPnP and ICMP. It needs mesh network topology to function properly. To selectively grant and revoke access rights, a decentralized exchange of identification attributes reclaim ID is used, using the GNS (GNU Name System) and attribute-based encryption (Attribute-Based Encryption).
HOW GNS IS BETTER THAN DNS ?
The main concept at the base level i.e. recursive resolving is same to that of DNS but there is a difference in their working. In the traditional domain name resolving, let us suppose if we want to resolve www.ethicaldebuggers.com, then first the query will go to the root server where it will define the address of the Top Level Domain. When it reaches to the address of TLD, then it resolves the further domain name and finally determines the destination IP address. So it means ,here all the information got public. All resolver which are involved in resolving the domain name in the entire path will share the information about DNS. But GNS keeps all this information private.
Now in GNS- GNU name system, all the work is done through distributed hash table. Distributed Hash Table(DHT) is installed in each resolver on the network. So when a query is made by the client to resolve a domain name system in GNS, it will send the query to the starting zone. The zone here is the pair of private key and public key of the origin and destination resolver represented as d- origin resolver’s private key and zk-destination resolver’s public key respectively.
The DHT here maintains all the key pair values on each resolver and thus using the concept of asymmetric cryptography, resolvers at different level do not know that to which they have to transmit the query in the resolution process.
Resolver at each level using Hash tables determines the public zone key delegate to which they have to transmit the query. The cryptography uses a ECDSA scheme based on Curve25519 elliptic curves. It is an elliptic curve offering 128 bits of security and designed for use with the elliptic curve ECDH key agreement scheme. The eleptical curves again are the mathematical equations which forms a complex cryptographic algorithms.
These are the some of the GNS records that are queried across the resolvers:
- PKEY- Public key of the corresponding resolver
- GNS2DNS- Every resource record contains the DNS information for DNS resolving.
- LEHO- Legacy Host name records that is used by the GNS to map with DNS host name in a legacy network.
- BOX- It is a record which stores all the information related to a particular domain like its subdomains.
- NICK- It is a nickname of the other zones to indicate which public key indicates to what